Omnipod® 5 Shows Significant Improvements in Glycemic Measures and Diabetes Distress

Omnipod 5 is the first automated insulin delivery system (AID) FDA cleared for patients with type 2 diabetes in the US. It is also the first and only tubeless AID system in the US. A single arm, multicenter prospective study by Pasquel et al. evaluated the safety and efficacy of the Omnipod 5 AID System in adults with type 2 diabetes. 1
Key Takeaways
- Omnipod 5 lowered A1C regardless of patient race, ethnicity, GLP-1 use and whether they were carb counting or not. In patients with a baseline of A1C ≥9%, the A1C was lowered by 2.1% (-0.8 in full study population)
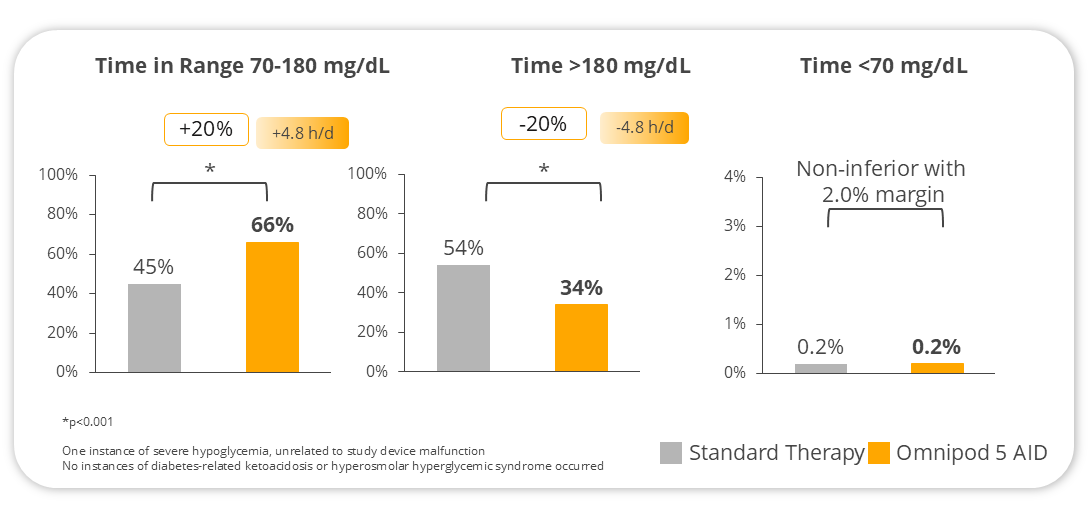
- Participants spent more time in range by nearly 5 hours a day (% of time spent between 70-180 mg/dL)
- No increase in time in hypoglycemia (% time spent <70 mg/dL)
- 29% reduction in insulin need
- Significant reduction in patient-reported distress related to diabetes, and improved quality of sleep were observed
Study Overview
The study consisted of a standard therapy phase of 14 days where participants continued using their pre-study therapy. During this time, investigators assessed insulin dosing at mealtimes and provided carbohydrate counting education or advised participants to use a simplified meal bolus strategy (ex: small, medium and large, fixed dose, or correction-only). Following that, participants transitioned to the 13-week treatment phase using the Omnipod 5 AID System.
The study design purposely defined enrollment goals to enroll a higher proportion of non-white participants to encompass communities affected by social determinants of health, who also have higher prevalence rates of diabetes and have often been underrepresented in clinical trials as shown in Figure 1.
Participants were aged 18-75 years and treated with a stable insulin regimen for at least 3 months prior to screening. They could additionally be treated with other antihyperglycemic and weight loss medications without dose changes for at least 4 weeks prior to the trial. All participants were required to have a baseline A1c of less than 12%, and for basal insulin only users, there was lower A1c limit of 7%. There was no limit to the participants’ total daily insulin dose.
Of the 305 initiating AID, prior therapy diversity at baseline included:
- 73% on MDI
- 6% on an insulin pump without AID
- 21% on basal insulin only
- 68% were using CGM
- 55% on GLP-1RA
- 44% on SGLT-2i
- 27% on both GLP-1RA and SGLT-2i
- 41% of the participants had publicly funded insurance or no health insurance