Insulin Pumps, Explained
So… what’s an insulin pump?
An insulin pump is a small, wearable gadget that can deliver insulin continuously throughout the day and night, often in very small doses. Insulin pumps can help manage blood glucose levels.1
Insulin pumps are an alternative to multiple daily injections (MDI) for people with diabetes.
They are becoming an increasingly popular choice for people with type 1 diabetes, but that doesn’t mean that they suit everyone.
Although insulin pumps eliminate the need for MDI, the recommendation is to still carry a back-up pen or syringe & insulin vial, in case of emergencies.
Different types of insulin pump
There are a few different types of insulin pump. Let’s take a look!


Tethered pumps
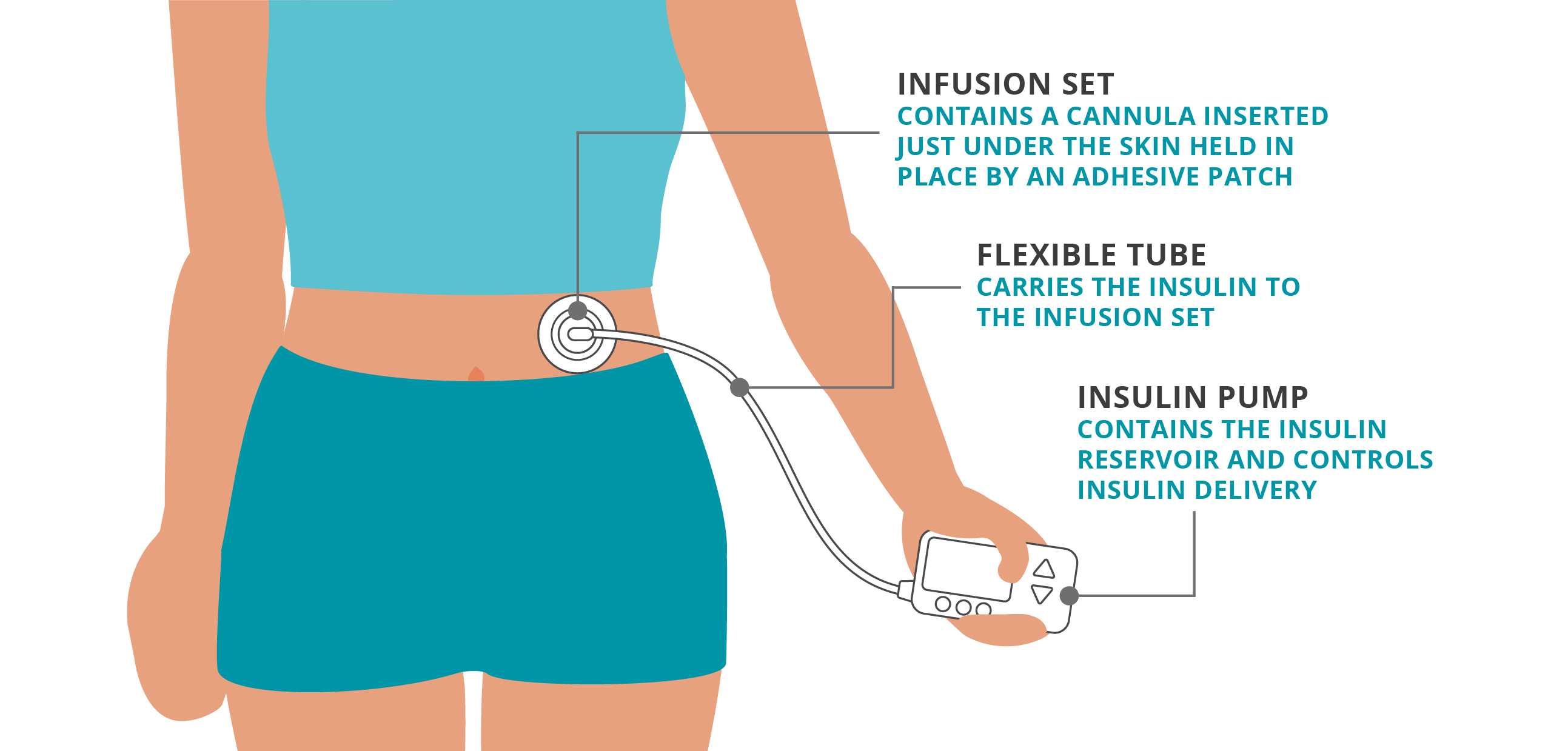
A tethered pump is sometimes called a tubed pump. It has a thin tube that connects the pump itself - which contains the insulin - to the body via an infusion set with a cannula. Insulin is delivered through the tube, and the pump can be kept in your pocket, or clipped to a belt or bra.

Patch pumps
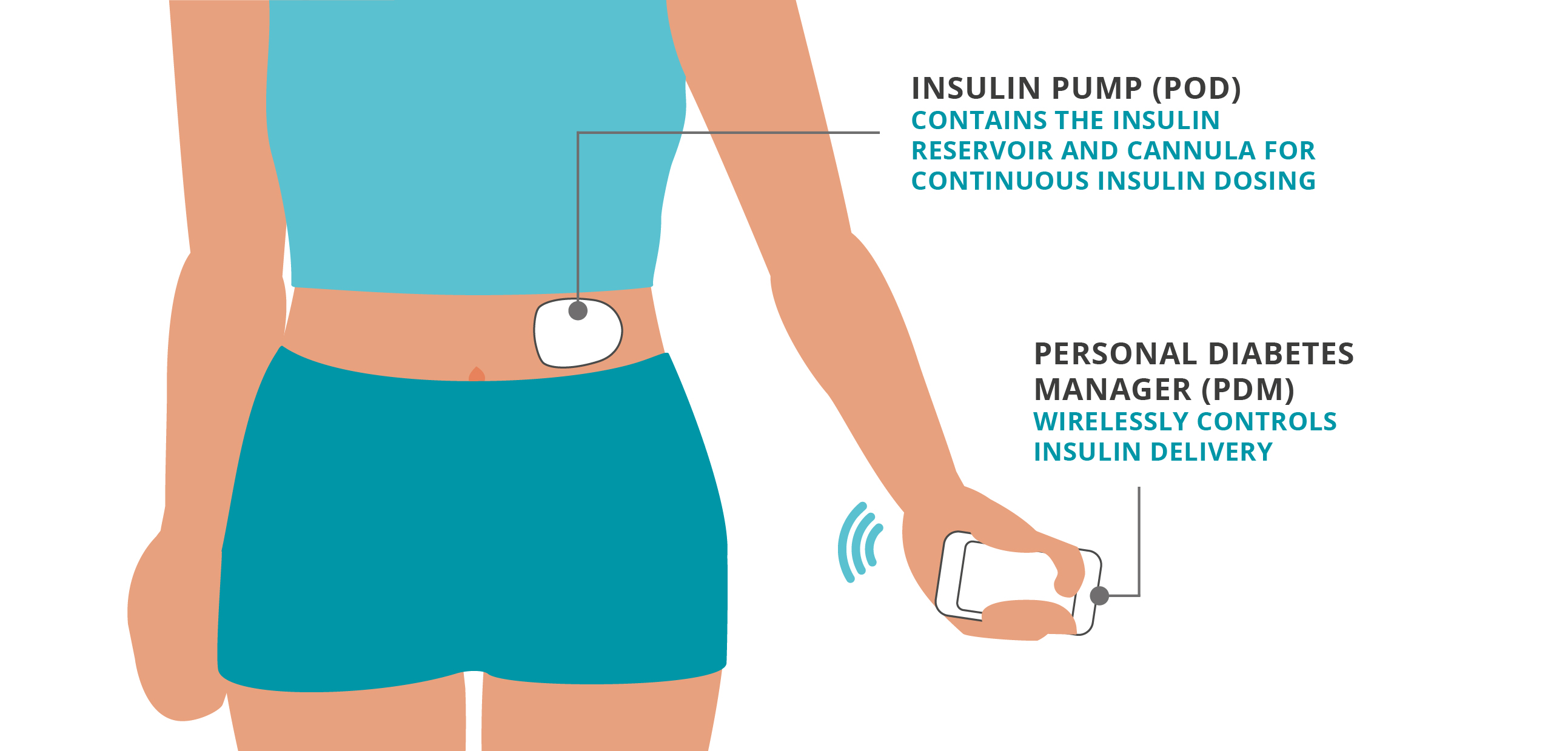
A patch pump is sometimes called a tubeless or wireless pump. The part that contains the insulin is stuck directly to the skin with adhesive, so there is no connecting tube. You can wear a patch pump almost anywhere you would administer an insulin injection. Insulin dosing is remotely programmed from a separate device a bit like a remote control.
How does an insulin pump work?
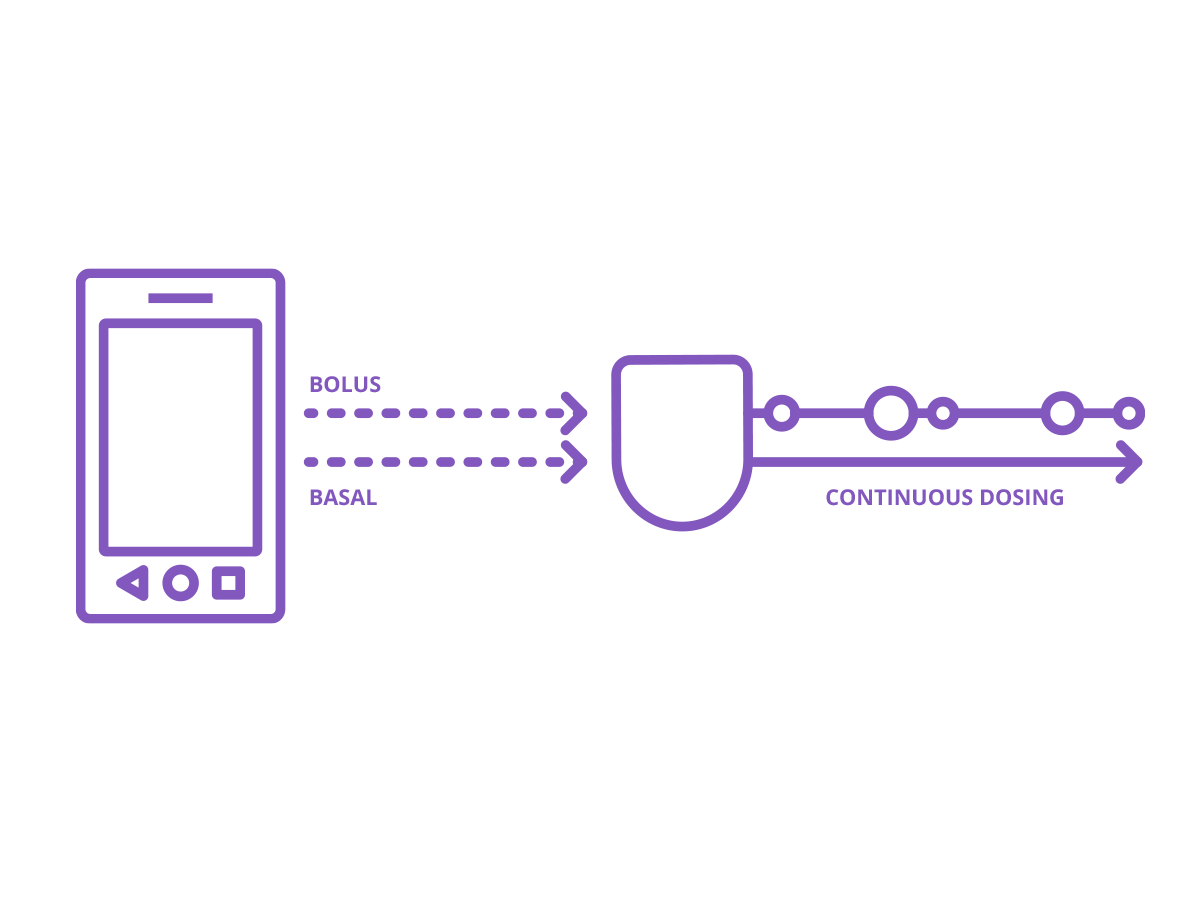
A continuous amount of insulin is delivered 24 hours a day through a cannula placed under the skin. This is known as a basal dose, but it’s sometimes called background insulin.
Additional insulin is delivered for meals and blood glucose corrections - these are known as bolus doses.2
Traditional pumps

Tubeless pumps

Some insulin pumps can help you calculate your bolus dose (yay!). These will be based on a combination of your personal settings, glucose reading and the carbohydrate values for any food you’re eating.
You only need one type of insulin with an insulin pump, commonly known as fast-acting insulin. This is used for both your basal and bolus doses.
A bit more about basal rates
Let’s talk about bolus insulin
Frequently Asked Questions about Insulin Pumps
Who qualifies for an insulin pump?
Are insulin pumps painful?
Can I shower with an insulin pump?
Do you sleep with an insulin pump?
Do I still need both types of insulin?
How much does it cost?
It all sounds pretty good so far, doesn’t it? But choices around diabetes management are very personal, and people may look for different features in an insulin pump. The NDSS provides some information on the key considerations around accessing partially subsidised insulin pump consumables.
Next up...
Let’s get more into the specifics of how the Tubeless Omnipod® Systems work. Rather than “Pump therapy” we call it “Tubeless, Pod Therapy”
These modules are not a replacement for medical advice or training. Please always speak to a qualified healthcare professional about your options.
References and disclaimers:
1- Ravi Retnakaran, Jackie Hochman, J. Hans DeVries, Helene Hanaire-Broutin, Robert J. Heine, Vincent Melki, Bernard Zinman; Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Versus Multiple Daily Injections: The impact of baseline A1c. Diabetes Care 1 November 2004; 27 (11): 2590–2596. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.27.11.2590
2- Walsh J, Roberts R. Pumping Insulin. 6th ed. San Diego, CA: Torrey Pines Press; 2017.
3- JDRF. (2023, August 22). Insulin pumps. jdrf.org.uk/information-support/treatments-technologies/insulin-pumps. Retrieved March 13, 2024, from https://jdrf.org.uk/information-support/treatments-technologies/insulin-pumps/#:~:text=What%20is%20an%20insulin%20pump,down%20high%20blood%20glucose%20levels.
4- Jill Weissberg-Benchell, Jeanne Antisdel-Lomaglio, Roopa Seshadri; Insulin Pump Therapy: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 1 April 2003; 26 (4): 1079–1087. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.26.4.1079